Notes on the Mulligan/Cheating Climate
One of the unexpected things you learn when you run a large high-stakes online exam is that the data starts revealing things the test was never designed to measure.
As CLT has grown, especially with more public school participation, one of the clearest insights has been around cheating.
The sad truth is that public school students are not just slightly more likely to cheat. They are dramatically more likely to attempt cheating than students from classical schools, religious schools, or homeschool backgrounds.
This shouldn’t be surprising.
Most public schools operate with no clear moral or philosophical framework for why cheating is inherently wrong. If education is just about the score, cheating simply becomes part of the game.
——-
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
Taxpayer Funds and Open Records
If the Legislature’s intent is to protect sensitive NIL agreements involving student-athletes, the language should be narrowly tailored to accomplish that goal,” Bennett said.
Lynch said the bill wouldn’t provide an unlimited exemption. The university has released records that don’t involve student privacy or competitive interests, including the athletics department budget and information reported to the NCAA. This legislation wouldn’t change that, she said.
The bill would support UW-Madison’s continued denial of certain records, such as NIL contracts between the university and student-athletes, and UW-Madison’s NIL contract template, she said.
“I acknowledge (the exemption) may look like it’s broad, but I also can’t predict the future,” Lynch said.
The university needs flexibility to respond to potential NIL changes, she said.
“Children not raised in two parent homes struggle on many dimensions”
Wisconsin continues to lead the nation in the racial achievement gap between white and African American students. According to the 2024 National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) in fourth grade reading, Wisconsin’s 45-point gap is the largest in the country—13 points greater than the next grouping of states such as Louisiana, Michigan, and South Carolina. State-level data from the Forward Exam mirrors these national results, revealing persistent and deep differences in academic proficiency. While many policymakers attribute these gaps to explicit racism, historic discrimination, and systemic inequities, this analysis investigates the extent to which other factors—specifically poverty and disability status—help to explain the relationship between race and academic performance.
More.
What’s been the result of DEI, CRT, SEL, restorative justice, abandoning discipline, ignoring truancy, lowering standards, binging on taxes and debt, hiring more and more administrators & non-teaching staff, and constantly obsessing about race?
——-
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
Civics: “just as this year and in the previous cycles, there will be no meaningful choice”
But the message is clear: once again in 2027, just as this year and in the previous cycles, there will be no meaningful choice. By that time there will be five partisan liberals on the court and Brunette will run promising to be the sixth. By August of 2027 there will be only one conservative, Brian Hagedon, among the seven justices.
Of course, Republicans will nominate someone to run against Brunette, but it won’t matter. Liberal Democrats now own these seats. Two things happened. First, liberals became super-charged about these court races when they figured out that they weren’t going to take back the legislature any time soon, but they could legislate through the court. Then even the supercharger went into overdrive after Roe was overturned. The second thing that happened is that the demographics switched. It’s voters with more years of education who show up to vote in spring elections. Those used to be Republicans, but now they’re Democrats. The Republicans are now the blue collar party while the Democrats are the college-educated.
“ai” & academia
My two posts on AI in academia got over a million views and a thousand angry responses. I got a few things wrong. I stand by the rest. But most people reacted to the headline, not the arguments.
So here are all 20 theses laid out. Tell me which ones you actually disagree with 🧵
School District Governance and Girls’ Privacy
The Quote: WILL Deputy Counsel, Cory Brewer, stated, “This is a welcome decision by the Trump Administration to enforce Title IX and protect girls’ privacy. For too long, school districts in Wisconsin have allowed policies that force young girls to share private spaces with biological males. The Department of Education should continue to press for full enforcement of Title IX across the state. We have already filed a Title IX complaint against Westosha Central High School and are hopeful the federal investigation into the Sun Prairie Area School District will bring accountability.”
WILL’s Fight for Student Privacy: WILL has filed Title IX complaints against Westosha Central High School and the Sun Prairie Area School District (an investigation opened in 2023 is still pending) following concerns from parents that biological boys were using the girls’ private locker rooms and bathrooms.
Parents are pushing back on screens in the early grades
A few months before her daughter started kindergarten, Claire Benoist saw a Facebook post that stunned her. Another family with an incoming kindergartner was wondering if it was true that children in the Croton-Harmon School District, 45 miles north of New York City, receive an iPad when they start school.
Other parents confirmed this: Kindergartners are often on their own iPads during school, playing games and watching television shows and YouTube videos. “It had never occurred to me that screens would be used in such a way,” Benoist said.
A few weeks before school started, Benoist told school administrators in the 1,500-student district that she couldn’t believe schools would give devices to kids as young as 4 and 5. Benoist and her husband had followed pediatric guidelines recommending no screen time before age 2. After that, they only allowed occasional episodes of kids’ shows like “Bluey” or “Daniel Tiger’s Neighborhood.”
School administrators assured Benoist that iPad time would be limited to 15 minutes a day, she said. But once school started, Benoist’s daughter suddenly knew jingles from diaper and car commercials, which Benoist and her husband determined were playing before YouTube videos at school.
“It feels like too much,” said Benoist, whose daughter has watched videos during snack time, transition time and dismissal.
The Computer Science job market tells two stories, not one.
The numbers explain why. CS degrees doubled from 52,000 to 113,000 per year over the last decade. Universities kept expanding enrollment because the demand signal from 2021 said “hire everyone.” Then three things happened simultaneously: tech companies overhired, corrected with 250K+ layoffs across 2024-2025, and started replacing junior engineering tasks with AI tooling. The entry-level funnel collapsed while the supply pipeline was locked in at peak capacity.
CS unemployment for recent grads hit 6.1% in 2025. That’s nearly double philosophy majors at 3.2%. The “learn to code” era produced a generation of graduates competing for jobs that are either gone or now require 3+ years of LLM integration experience they couldn’t possibly have.
The split is geographic and institutional. If you’re at a top-15 program in a tech corridor with two internships on your resume, the market looks tight but navigable. If you’re at a mid-tier state school with no internship pipeline, you’re watching the career fair fill up with insurance companies while your $140K in loans accrues interest.
That faculty meeting fight about “pivoting to AI collaboration skills” is the right debate happening two years too late. The schools that retooled their curriculum in 2023 will survive. The ones still teaching data structures as the core value proposition while job postings demand LLM orchestration are training students for a market that no longer exists.
Affirmative action in Medicine : A forbidden debate?
As a young boy, I grew up reading of the triumph of good over evil in my favorite Indian comic book: Amar Chitra Katha. The tales of the virtuous vassals imbued by a godly spirit vanquishing the forces of darkness is powerful and appealing in large measure because we believe we inhabit a world where the good guys won. But unlike the comic books, the bad guys in the real world don’t have horns, and don’t look like J.R.R Tolkien’s trolls – they wear suits and have fancy degrees and appear quite respectable. Would it be really obvious if the bad guys won? History is after all replete with examples of revolutionaries who believe themselves to be virtuous, blindly following a degenerate elite into an amoral abyss.
With this in mind, a lawsuit from the world of American medicine, filed by Dr. Norman Wang against his employer and others is particularly enlightening.
This particular affair began when Dr. Wang published a paper in the Journal of the American Heart Association titled “Diversity, Inclusion, and Equity: Evolution of Race and Ethnicity Considerations for the Cardiology Workforce in the United States of America From 1969 to 2019 “. The purpose of this white paper was to “provide an overview of policies that have been created to impact the racial and ethnic composition of the cardiology workforce, to consider the evolution of racial and ethnic preferences in legal and medical spheres, to critically assess current paradigms, and to consider potential solutions to anticipated challenges.”
At the time of the publication in March 2020, Norman Wang was a cardiologist, a member of the faculty of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and director of the fellowship program in clinical cardiac electrophysiology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC). His publications to this point had largely consisted of esoteric matters in the field of his expertise : electrophysiology. This publication, was of an entirely different nature. The article asserted that the medical profession had not been successful in its overarching goal of increasing the percentages of underrepresented races and ethnicities in the medical profession, and particularly in cardiology. The article also noted that programs to achieve these diversity goals applied different standards to applications by members of underrepresented races and ethnicities and thus raised questions about the legality of doing so because of how race was being used as a factor in hiring, recruitment, promotion and admissions.
The Public Schools: Worse Than You Think
If you think America’s public schools are terrible, you are right. If you think they lean to the left in their instruction, you are also right. But the truth is much worse. Guided in large part by radically left-wing teachers’ unions, our schools are in some cases openly rejecting the teaching of “content”–the word used in my state, Minnesota–in favor of requiring activism.
Check out this American Experiment video on Liberated Ethnic Studies:
k-12 tax & $pending climate: Grant industrial complex notes
The clearest example yet of what the Deep State looks like: unelected bureaucrats refusing access to an executive branch agency for representatives sent by the newly elected president—the one in whom our Constitution says the executive power is vested.
There needs to be accountability for these actions, or we will continue having a shadow fourth branch of government wholly unaccountable to the will of the American people.
——
The growth of the administrative class in every regulated industry has been breathtaking.
UW-Madison lukewarm on 3-year degrees despite UW system’s blessing
Wisconsin’s 13 public universities can now develop three-year bachelor’s degree programs — but it could be a while before any appear at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
“I know there are some other UW institutions that are exploring that as a possibility. We have not had discussions here at Madison about that,” Allison La Tarte, UW-Madison’s vice provost and chief data and analytics officer, said at a recent campus meeting.
Interim Provost John Zumbrunnen added, “I do not see (UW-Madison) any time soon turning towards the widespread presence of reduced-credit bachelor’s degrees.”
The UW system’s Board of Regents revised its policyThursday, allowing campuses to explore reduced-credit programs. Students could earn a bachelor’s degree with at least 90 credits rather than 120.
The VC Who Went to War With His School Board, and won
When 80% of parents wanted in-person learning and got virtual school instead, venture capitalist Paul Martino discovered his job description had changed: he was now doing the superintendent’s job for him.
In August 2020, Paul Martino wasn’t looking for a fight. He was looking for answers.
The Central Bucks School District — Pennsylvania’s largest public school district — had just announced a switch to virtual learning, despite a survey showing over 80% of district parents preferred in-person education. Martino, whose kids were 9 and 11, felt something snap.
“It happened out of pure anger.”
That anger became action. Martino, a venture capitalist by trade, launched a grassroots movement that would ultimately lead to the superintendent’s resignation and school board member replacements. More importantly, it sparked a template that parents across the country would follow to reclaim their voice in their children’s education.
“We ended up putting the school board on notice that we were paying attention,” Martino recalls. Soon, his phone was ringing with calls from around the country asking the same question: How did you do that?
* The average was 64/100.*
just gave a closed-book, pen-and-paper midterm exam in my 300-level course at UBC with 100 students. All exams were graded by an experienced graduate-level TA according to a rubric.
My class averages at UBC are usually 80-85.
Context:
- This was the first midterm, covering ONLY 4 weeks of material.
- Students had a list of possible questions in advance: no surprise questions.
- Questions included (a) 3 concept definitions, (b) 3 paragraph-long questions, and (c) a 1.5-page essay.
- I have taught this class multiple times. Nothing in my teaching style changed this semester.
- We read entire paragraphs of text in class, so students don’t have to do something on their own that wasn’t covered during the lecture.
- Students take a 10-question multiple-choice quiz at the end of every class (30% of the final grade).
- Attendance is 95-99% every class. Attention during lectures and participation in pair-work activities are very high → anticipating the end-of-class quiz.
* But unfortunately, I suspect many students are not reading the material on the syllabus. They are asking LLMs to summarize it instead.*
Parents Are Spending Big to Optimize Their Babies’ Microbiomes
Allen and her son are at the vanguard of a fast-growing business catering to health-conscious parents. Companies are offering products they said can alleviate gastrointestinal issues common in infants, and help optimize young children’s gut microbiomes.
Some scientists said that infancy can be a critical period to shape the microbiome, and potentially prevent disease and improve health later on. But microbiome researchers and pediatricians said that many of the products’ marketing is outpacing the science.
Selling baby-biotics
Tiny Health and Alba Health sell gut health tests for babies for $249 and $349, respectively. Parents send in stool samples and the companies return detailed analyses of the types and prevalence of various microbes found. The companies also offer recommendations, like giving certain supplements or bringing babies to a petting zoo, which they said can improve children’s microbiomes.
Infant formula and baby food producers are incorporating more prebiotics, which fuel beneficial gut bacteria. They also are adding probiotics, the beneficial bacteria itself.
Wisconsin NIL Legislation’s Language Casts Wide Net of Secrecy
A college sports bill burrowing through the Wisconsinstate legislature could shield all financial records involving the University of Wisconsin’s athletics department and those of other public institutions in the state.
Such is the warning from transparency advocates over Assembly Bill 1034, which passed the lower chamber last month by a 95-1 vote. A companion measure, Senate Bill 1075, is now pending in the Wisconsin state Senate, where last week it received a public hearing before the committee on government operations, labor and economic development.
The legislation is designed to align state law with the House v. NCAA settlement by establishing the right of the University of Wisconsin System to pay college athletes for their NIL. The bill would also increase state funding to cover debt service for maintenance of certain athletic facilities at UW, UW-Milwaukee and UW-Green Bay. Lastly, it would make explicit that athletes who sign revenue-sharing deals with private institutions like Marquette would not be rendered employees of those schools as a result.
The bill has been strongly endorsed by UW, which has argued that it is necessary to help ensure its athletic programs remain competitive amidst the “volatility in college athletics.”
New Hampshire School Meetings question
At our regional cooperative school district budget meetings, a group has been repeatedly requesting secret ballots on amendments as a delay tactic. The counting process runs out the clock and forces voters with time commitments to leave before the vote. I started looking into whether secret ballots are even legally required here, and I don’t think they are.
RSA 40:4-a is the only NH statute giving voters the right to demand a secret ballot, but it only applies to town meetings. It does not extend to school district meetings. RSA 197, which actually governs school district meetings, contains zero voting procedure rules. RSA 195, covering cooperative school districts specifically, is equally silent. RSA 197:19 gives the school district moderator town-moderator-equivalent powers, but that is the moderator’s authority, not a voter right to demand secret ballots.
My conclusion is that secret ballots at these meetings are moderator discretion and local custom, not a statutory requirement. If correct, the meeting body could vote to change the procedure themselves.
Am I missing a statute that creates this right specifically for school district deliberative sessions?
Not a lawyer. This is really the first time I have tried to read statutes.
Notes on $pending and outcomes
Here’s a quick summary of a thread I recently posted on both BlueSky and X.
Storytime – for those who want to push some “southern” miracle in public schooling – using Mississippi as their exemplar, and implying “red state” strategies are the policy solution:
First – Mississippi doesn’t catch Massachusetts or New Jersey. NOT EVEN CLOSE
But states like Arizona and Florida fall to and even blow Mississippi in some cases on 8th grade NAEP performance (a better indicator of the cumulative effects of a system on student learning than 4th grade assessments).
Notable in these graphs are the continued large declines in Arizona and Florida while others are stabilizing or rebounding from 2022 to 2024 (AZ stabilizes in math, but not FL).
‘Terrifying’: Family says Evanston-born U.S. citizen detained for hours after returning to O’Hare
Outside the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement facility in suburban Broadview on Sunday, Sarah Afzal spoke on behalf of her 28-year-old sister, Sundas Naqvi, who goes by Sunny.
Elected officials, family members and Sunny’s attorney stood alongside her, sharing their accounts of what they say happened after Sunny returned to Chicago.
Afzal says Sunny, a U.S. citizen born in Evanston, was detained by U.S. Customs and Border Patrol at Chicago’s O’Hare International Airport while returning from Turkey on Thursday.
“Detained with no cause. All she was told was that there was curious travel history,” said Cook County Commissioner Kevin Morrison.
Afzal says Sunny was held at the lower level of Terminal 3 at O’Hare for nearly 30 hours along with five of her colleagues. Two of them are also U.S. citizens and three are green card holders.
The group had originally been headed to India for a work trip with a layover in Turkey, but the trip was canceled after visa issues came up while they were there. They split up and traveled to different countries in the region, with Sunny going to Bulgaria and Austria. The group later reunited in Turkey and flew back to Chicago on Thursday morning.
Faculty Perspectives on Academic Freedom, Free Expression and Campus Climate at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
Executive Summary
This survey of tenure-track and tenured faculty at UW–Madison examines the ideological composition of the faculty, attitudes toward hiring, perceptions of campus climate, and experiences with expressing controversial opinions.
Ideological Composition
UW–Madison faculty are substantially more liberal than both the general American public and Americans with doctoral degrees. Seven in ten faculty identify as some form of liberal, while fewer than one in ten identify as conservative. This imbalance is present across all academic fields, though it varies in degree, with the Humanities showing the highest concentration of liberal faculty. Economics-related fields stand out as having more ideological diversity than other social sciences, though they still lean liberal overall. Junior faculty are more liberal than senior faculty, raising the possibility that the imbalance may increase over time. Notably, faculty of color are not more liberal than white faculty—and Asian faculty are significantly more likely to identify as conservative—indicating that efforts to advance racial diversity and viewpoint diversity need not be in tension.
Hiring
Using a randomized survey experiment, the study finds that significant minorities of faculty would be less likely to hire a candidate who expressed a conservative view on topics such as immigration, abortion, affirmative action, or transgender sports participation. Because respondents were randomly assigned to evaluate either a liberal or conservative statement, these differences cannot be attributed to a general aversion to candidates expressing political opinions. The asymmetry specifically reflects less favorable treatment of conservative viewpoints, with differences ranging from 11 to 38 percentage points depending on the topic.
Consequences for Expression
While liberal faculty are more likely to express controversial views, conservative faculty who do express views report experiencing institutional consequences—such as warnings from administrators—at substantially higher rates than liberal faculty who express views.
Notes on the future of the Institute for Education Sciences
Thank you, Amber! My colleague Amber Northern, Fordham’s longtime senior vice president for research, has done American education a great service by recommending a future for the Institute for Education Sciences that goes far beyond undoing the damage done by DOGE a year ago.
On sabbatical from Fordham for seven months and—at the invitation of Secretary McMahon—detailed to the U.S. Department of Education under the Intergovernmental Personnel Act (IPA), Amber, with help from a solitary research assistant (plus beaucoup interested parties, some invited, some self-invited), produced a 95-page report, subtitled “a strategy for relevance and renewal,” which the powers-that-be, after some dithering, finally made public on Friday at mid-day. Endorsements from those powers were cordial but guarded, as you can see in the accompanying press release, though acting IES director Matthew Soldner separately issued a thoughtful and supportive message via blog.
That’s because, as best one can tell from outside, the administration itself has made no decisions about what actually to do with IES—as it gradually seeks to “eliminate” the Education Department itself, so far by cutting staff, attempting to cut budgets, and outsourcing various programs and duties to other agencies. This silence—or indecision, political wariness, whatever—serves, of course, to make the entire education field less trusting and confident regarding future developments. (Meanwhile, Congress keeps adding funds to various IES activities—and other Department programs—that the White House keeps trying to shrink or zero out.)
How to think about reconstructing IES’s central function within that unwanted department—especially with vast uncertainty as to whether Congress will ever update the aging (2002) Education Sciences Reform Act that created IES? Many of the reforms proposed by Amber could be undertaken under current law, but several major recommendations would require legislative action “should Congress choose to reauthorize ESRA.” These include building a lot more flexibility for states into the “regional labs” program and empowering IES to do direct procurements of cutting-edge projects rather than struggling through the department’s glacial grants-and-contracts unit.
Civics: “Enemies like Iran will exploit liberal naivety until we’re destroyed”
He realised that the liberal traditions of tolerance and freedom, while valuable, had an Achilles’ heel: they can be turned against you. In his book The Open Society and Its Enemies, he articulated the most pertinent diagnosis of his age and perhaps ours, too: “Unlimited tolerance must lead to the disappearance of tolerance. If we extend unlimited tolerance even to those who are intolerant [such as Nazis] … then the tolerant will be destroyed, and tolerance with them.”
I suggest we see this pattern afresh today. The legal immigration systems of western democracies have been described as “welcoming” and “liberal”, but in the name of freedom and tolerance we have opened our doors to those who hate these values and wish to destroy them. The names of Abu Qatada, Omar Bakri Muhammad and Abu Hamza are perhaps familiar; worse, because more widespread, are the dangers of Muslim bloc voting and creeping sharia. It is nether racist nor divisive to state that this is a form of self-annihilating madness dressed up as enlightenment. Yes, it’s true only a minority of western Muslims are Islamists; but it is also true that we have utterly failed to confront those who are. We have effectively been made to pay taxes to fifth-columnists who wish for our demise.
——
Britain’s ‘national treasures’ have adopted a suicidal empathy for Islamist nutjobs and religious fundamentalists.
High Schools Are Losing the Struggle to Block Pot—Even During Class
Liberty High is on the front lines of a battle to keep weed out of American high schools. It’s an uphill one. California legalized medical marijuana in 1996, the first state in the country to do so. Recreational cannabis has been legal in the state since 2016, with retail sales beginning in 2018, when Liberty High’s current seniors were still in elementary school. Now, 24 states plus Washington, D.C., have legalized marijuana for recreational use.
While the legal age to buy recreational marijuana is 21 in California (It’s 18 for medical marijuana), students said it is relatively easy to get from older siblings, friends and acquaintances. Dispensaries often offer delivery, requiring adults to show valid ID.
Legalization has shifted how cannabis is perceived, from a way for stoners to get high to a mainstream health and wellness tool. Cannabis companies now market their wares as treatments for anxiety, pain and sleep problems. Edibles in cute packaging and THC vapes in flavors like “strawberry cough” and “Zkittles” (a play on the candy) can make marijuana seem safe, stylish and fun.
Weed is “seen as organic. It’s all-natural,” said Will Trimua, a 17-year-old Liberty High senior, about many of his peers’ views. And unlike nicotine, doctors sometimes recommend it, “so why should it be bad then?” added Trimua, who says he doesn’t partake.
Civics: Advertising Surveillance Enables Government Surveillance
The online advertising industry has built a massive surveillance machine, and the government can co-opt it to spy on us.
In the absence of strong privacy laws, surveillance-based advertising has become the norm online. Companies track our online and offline activity, then share it with ad tech companies and data brokers to help target ads. Law enforcement agencies take advantage of this advertising system to buy information about us that they would normally need a warrant for, like location data. They rely on the multi-billion-dollar data broker industry to buy location data harvested from people’s smartphones.
We’ve known for years that location data brokers are one part of federal law enforcement’s massive surveillance arsenal, including immigration enforcement agencies like CBP and Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). ICE, CBP and the FBI have purchased location data from the data broker Venntell and used it to identify immigrants who were later arrested. Last year, ICE purchased a spy tool called Webloc that gathers the locations of millions of phones and makes it easy to search for phones within specific geographic areas over a period of time. Webloc also allows them to filter location data by the unique advertising IDs that Apple and Google assign to our phones.
But a document recently obtained by 404 Media is the first time CBP has acknowledged the location data it buys is partially sourced from the system powering nearly every ad you see online: real-time bidding (RTB). As CBP puts it, “RTB-sourced location data is recorded when an advertisement is served.”
Civics: Newsom planning $19-million taxpayer funded push to polish California’s national image
Gov. Gavin Newsom plans to spend $19 million promoting California and dispelling “myths driven by misinformation and political rhetoric” in a marketing campaign that would run through the final months of his administration as he weighs a potential run for president.
The Governor’s Office of Business and Economic Development is seeking a contractor to design a statewide taxpayer-funded “California Brand Campaign,” with two-thirds of spending under the proposal to be used for paid advertising and media placements. Bidding on the contract opened Feb. 24 and is expected to end March 13.
K-12 Governance: “institutions who are behind, stay behind”
One of the more pathologically interesting facets of institutional evolution is how institutions who are behind, stay behind. Business analysts toss around the word ‘culture’ constantly. But what is Laggard culture? And how, if we inherit such an institution, do we do a meaningful turn-around?
In order to understand where to start, you have to understand what are the primary characteristics of a Laggard organization. A Laggard organization is one that consistently falls behind its peers, and seemingly is inured to meaningful change that would alter its status-based relationships with its peers. What this means that, especially in its upper-level administrative ranks, decisions are only made after other, more intellectually progressive orgs. have moved on from past historical patterns that may have provided success. It’s only when those other leaders have established a pattern of accomplishment that laggard organizations will then move in behind the leaders and adopt the ostensibly new successful patterns of operation.
There is no better place to observe this pattern of behavior than in academic institutions in the new milieu established by Donald Trump. With a series of Executive Orders, the Trump administration established, under no uncertain terms that the vast Diversity, Equity and Inclusion apparatuses built up to enshrine Woke Doctrine across all aspects of university life was to be dismantled, or lose all federal funding. This was actually affirmed, pre-Trump 2, by the Supreme Court in 2023, with the case Students for Fair Admissions vs. Harvard.
But the universities “fought back” — some kind of idiot euphemism that they weren’t going to dismantle their various DEI kingdoms, and “somehow” the public was going to rise up to defend the various machinations the universities had developed in the name of the various terms over the years. Academics screamed “academic freedom!” as well. But academic freedom, for the unwashed, means the ability to pursue intellectual paths inside the university, as long as it was a.) scholarly, and b.) somewhat defensible as far as being related to one’s focus of the home department, or related to a collaborative effort across the university, in pursuit of knowledge. Being one of the few that has actually exercised academic freedom (this blog is just the latest instantiation) I can tell you that most academics never come up against any boundaries where one would need to play that card.
This is actually a key identifying element of Laggard institutions — the obvious inability to change in the face of larger societal forces, while turning the entire apparatus of sophistication present in the organization into justifying the status quo. Inevitably, it’s wrapped in some kind of Communitarian v-Meme banner (“we CARE about our people.”). But the reality is it is a deeply tribal response that more maps to the Tribal/Authoritarian v-Meme structures most universities operate under.
Raise the Floor on Teacher Salaries
Earlier this week Matthew Yglesias wrote a piece on teacher salaries. He noted that:
…while New York pays 70 percent higher teacher salaries than Louisiana on average, its entry-level salaries are only 7 percent higher. That doesn’t come close to compensating for the higher cost of living. If you ask where “teacher” counts as a decent-paying job for someone just starting out, Mississippi and Louisiana look good and New York looks terrible, despite there being much higher average salaries in New York.
That observation raises a lot of interesting questions. But today I want to explore what happens when a state or district dramatically increases starting teacher salaries.
Let’s start with the state-level data. Consider the graph below. It shows the average teacher starting salary by state (left to right) versus the top salary (up and down). As the graph shows, states with higher starting salaries tend to also offer their teachers higher maximum salaries. Washington, California, and the District of Columbia pay the highest salaries regardless of a teacher’s experience level.
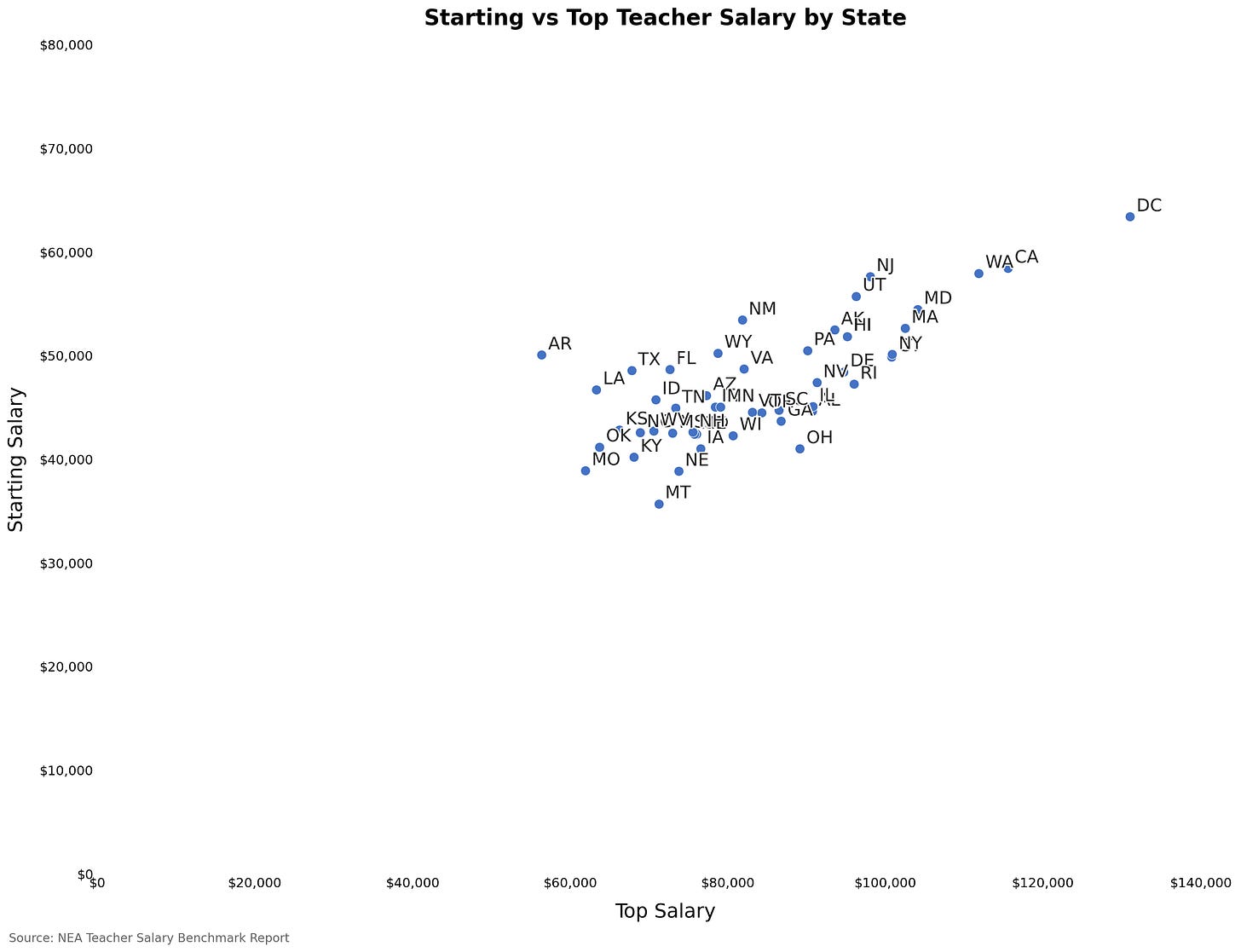
None of these are adjusted for cost of living. But now I want you to focus just on the starting salary aspect. I’ve added a red line to show something interesting. As of last year’s data, Arkansas schools offered nearly identical starting salaries ($50,031) as New York ($50,077). That’s a striking comparison given the huge differences in cost of living between the two states.
Teacher forced to resign for refusing to use ‘preferred pronouns’ gets $650,000 settlement
The nine-year-old case of an Indiana music teacher who refused to refer to students by their “preferred” pronouns and/or names has finally come to a conclusion.
In a settlement, the Alliance Defending Freedom reportsthe Brownsburg Community School Corporation agreed to pay John Kluge $650,000 after it (according to Kluge) forced him to resign his position.
The school district initially had compromised with Kluge on the matter, allowing him for about a year to call students by their last names.
But after “complaints of a few students and teachers,” the district changed its mind and Kluge said he was then threatened with being fired. He ended up turning in a letter of resignation, but withdrew it on the last day of the school year.
A visual guide to DNA sequencing
In the twenty years after the draft human genome was first released, the average sequencing cost per genome fell roughly one hundred thousand-fold, ending up just north of $500. In that same period, the cost to sequence a million letters or “megabase” of DNA fell to six tenths of a cent.2 This plummeting price is due largely to technological innovation, including new sequencing chemistries, computational methods for assembling raw reads into finished genomes, and highly efficient commercial sequencing machines.
Out of the many sequencing methods developed over the decades, five are particularly important. These are their histories.
“watched the system degrade into near-universal failure from 2001-2022”
In the last couple of weeks, I’ve gained a bunch of new followers, so I thought I’d just reintroduce myself.
I’m an ex-California public school teacher who watched the system degrade into near-universal failure from 2001-2022. My initial work was to explain the systemic incentives that have robbed millions of kids of a proper education. If you want to understand exactly how things have gone so wrong, I linked the first in a series of five articles explaining how the very structure of public school has been vaporized below.
My new goal is to bring you the simple structures I use in my day-to-day practice as a classroom teacher in a classical charter to get outsized gains in teaching kids what it means to be a Good American. (It’s slow work though because my nine-to-five is more like a seven-to-ten; that’s what it takes to scale this up to 150 kids.)
More will be coming soon. For now, if you have the stomach for it, the articles below will help you understand where we are so you can start building a Plan B for your family, even if you can’t fully exit the K12 system.
———
A Framework to Build Great Americans
A Great nation requires Great men and women. Greatness requires that we train our children to love what is good.
Princeton to consider proctoring for all in-person exams, a departure from 133 years of precedent
University faculty and administrators will consider a proposal to require proctoring for all in-person examinations, which would mark a departure from the traditionally unproctored exam format under the Honor Code. If passed, the policy could take effect as early as next fall, according to Honor Committee members.
The proposal was discussed in a meeting between Honor Committee leadership and Dean of the College Michael Gordin on Wednesday, Feb. 25. Although conversations about proctored examinations have been ongoing in recent years, the new policy is now set to enter a multi-stage faculty and administrative review before it can come to a vote by the faculty. Currently, only individual and small group examinations are proctored.
The tradition of not proctoring has existed since the introduction of Princeton’s honor system in 1893. The system has relied on student self-governance and mutual accountability. Students pledge both to refrain from infractions of academic dishonesty and to report any breaches of the Constitution they witness.
“The prohibition on proctoring is formalized in ‘Rules and Procedures of the Faculty.’ Any change to that policy would have to pass through the relevant committees and be voted on by the full faculty,” Gordin wrote in a statement to The Daily Princetonian. “Since that process has not begun, I cannot predict when it would conclude.”
On the College Board
This is amazing. This is the most well-researched indictment of the College Board cartel ever produced.
civics: Censorship Blueprint
“Safety”
As part of X’s incident response protocol, X initiated proactive manual sweeps to identify and remove violative content in less than 3 hours from the initial strikes. These sweeps have been running 24/7 since the response was initiated, and are supplemented by working group meetings bringing together experts across our company.
X is actively scaling its enforcement by building heuristics and Grok-based defenses that can detect and enforce against new forms of violative content that emerge on the platform. These defenses allow us to scale at speed, ensuring our users are protected in real time.
Florida Senate OKs bill to place new restrictions on public sector unions
A bill to make it harder for public sector unions to establish or renew their certification passed the Florida Senate despite arguments that it would impinge on workers’ constitutional rights.
The legislation, SB 1296, which is strongly backed by the anti-union Freedom Foundation, drew hundreds of union members from across the state to Tallahassee earlier this week to voice their opposition.
On Friday, five Republicans joined all Democrats in voting against the bill, which does not have the same language as the House, where it heads
——-
Related: Act 10
“SEIU is known in California political circles for pioneering and perfecting the art of extortion via ballot initiative.”
California ranks 48th in education.
——-
Six years on, country still waiting for a COVID reckoning
Six years after the coronavirus pandemic began to rip through the U.S., spreading death and sparking draconian shutdowns, the country still has not had a full accounting of the dystopian restrictions the government imposed to try to control the virus — and the public.
A coalition of civil rights groups says it’s time for that reckoning.
They have launched the COVID Justice Resolution, a call for Congress to officially repudiate government “overreach.” They say it’s not an attempt to assign blame — there’s enough to go around — but to reassert constitutional boundaries that slipped during the pandemic.
“There have never been any apologies,” said Jeffrey A. Tucker, a leader of the effort and founder of the Brownstone Institute. “These kinds of wounds are festering, and real, and widespread. I don’t believe there will ever be healing from what happened until we get some culturally significant institution saying very clearly ’This was wrong.’ That has to happen. And, think about it, it has not happened.”
———-
Civics: Woman sues Target for not hiring her because she has a pending robbery case
Courtney McElrath-Bey, 35, claims the company unlawfully used her background against her when it decided not to hire her for a warehouse position last year. Her lawsuit, filed in February and first reported by Legal Newsline, seeks damages and could expand to cover other applicants who were denied jobs under similar circumstances.
According to the complaint, Target extended McElrath-Bey a conditional offer in October for a job described as an “order picker or warehouse associate” contingent on the results of a background check.
Many Families Choose Public Schools Other Than Their Assigned Ones
Jude Schwalbach:
An analysis of 27 states and Washington, D.C. shows open enrollment is increasingly an attractive public school choice
K–12 open enrollment is a form of public-school choice that allows students to transfer from their residentially assigned district school to other public schools. Since open enrollment policies launched in the 1990s, they’ve been overshadowed by growth in charter schools, vouchers, scholarships funded through tax credits, and education savings accounts.
Most open enrollment programs, which now operate in 43 states, were initially weak, letting districts reject transfer applicants even when space was available. However, the post-Covid surge in school choice options created a renaissance in open enrollment policies. During state legislative sessions in 2025, three states—Arkansas, Nevada, and New Hampshire—enacted open enrollment laws, bringing the total to 17 states that have strengthened their open enrollment statutes since 2021.
Despite these improvements, most state laws remain lackluster. Just 16 states have universal cross-districtopen enrollment laws, which let students transfer to schools in other districts when extra seats are open, while only 17 states have universal within-district open enrollment laws that let students transfer to non-assigned schools inside their district when space allows.
Civics: “You don’t run a Constitutional republic on secret files”
“You don’t run a Constitutional republic on secret files,” added legal analyst Margot Cleveland.
A current government source said the prohibited access designation is “literally designed to hide files from Congress and from the FBI itself. It’s really frigging bad.”
Off-books surveillance and “disruption” of political figures in the Arctic Frost and Trump-Russia investigations comprise part of the find, but the files extend at least as far back as 1999, across Democratic and Republican Party presidencies, involving as many as a thousand distinct case numbers. There are no rules for passing access to the system from one administration to the next. Instead, operation of prohibited access files is described as an oral tradition passed down among senior FBI officials, independent of agents below and political appointees above in Congress and even the White House.
Here’s how the files came to light:
Activists have forced a medical college to pull the plug on a talk by one of the world’s leading figures in the youth gender debate
Approved, until it wasn’t
A talk to familiarise Australian family doctors with a safer treatment approach to youth gender dysphoria will not go ahead as planned after a medical college buckled to activist pressure.
The well-subscribed March 10 webinar presentation by Finnish psychiatrist Riittakerttu Kaltiala—a leading clinician and researcher in the international shift away from routine “gender-affirming” medicalisation of minors—had been approved and advertised since the New Year by the Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP).1
GP Louise Kirby, who was among the more than 200 subscribers who signed up for the RACGP event, told GCN—
“We’ve reached a point where presenting outcome data is called harmful, and where speaking out to protect children from irreversible, damaging interventions is incorrectly framed as an attack on children. That inversion should alarm every clinician”.
Professor Kaltiala set up paediatric gender services in Finland 15 years ago on the strength of promising results reported by the famous Amsterdam gender clinic, which pioneered the puberty blocker-driven “Dutch protocol” of gender reassignment for minors.
The feminization of autism
Sexual equality works in mysterious ways. Not only must we have equal pay and education, but it seems there must be equality in mental disorders as well. Or so I concluded about 15 years ago, when I started hearing about the large number of autistic females — previously undiagnosed — whose presentation differed markedly from the largely male stereotype, but who somehow had autism too.
This seemed to me quite strange. A condition with no biomarker, diagnosed mainly by the presence of certain distinctive behaviors — significant deficits in communication, rigid patterns of thought, repetitive activities, obsessive interests, and so on — now attributed to a new population on the basis of very different behaviors. The solution to my incomprehension, I was told, was the concept of “masking”. Women and girls were better at hiding their antisocial tendencies, a fact which made them profoundly anxious. Languishing neglected behind deceptively sociable masks, a much larger group could now be members of the club too.
This all sounded suspiciously convenient, tying in with modern fairytales of personal authenticity and the supposed tragedy of hiding “who you really are”. We are all masking things about ourselves; Jung would call it having a persona. And many introverts find social engagements confusing and exhausting. More to the point: if someone is mentally agile enough, both to notice her own social deficits and then seamlessly compensate for them, why are we treating this as autism at all?
Large genome model: open source AI trained on trillions of bases
..The researchers trained two versions of their system using a dataset called OpenGenome2, which contains 8.8 trillion bases from all three domains of life, as well as viruses that infect bacteria. They did not include viruses that attack eukaryotes, given that they were concerned that the system could be misused to create threats to humans. Two versions were trained: one that had 7 billion parameters tuned using 2.4 trillion bases, and the full version with 40 billion parameters trained on the full open genome dataset.
Milwaukee Reduces k-12 staff after significant tax & $pending increases
Milwaukee Public Schools announces plans to cut more than 260 positions in its effort to close a $46 million budget gap.
The proposed cuts include eliminating some assistant principals, deans of students and interventionists
Following the news that MPS overspent its budgetfor the last school year, putting the district about $46 million into the red, Cassellius said she needs to make cuts in order to pay off the deficit and craft a balanced budget plan for the next school year.
The Wrong Investigation of a Madison School Board Member
Maia Pearson, the chair of Madison’s police oversight board and a Madison school board member, has been charged with criminal misdemeanors related to her resisting arrest in an incident in downtown Madison in December.
In a criminal complaint, it is alleged that she and her friend, Urban Triage executive director Brandi Grayson, verbally abused staff at a theatre and then physically resisted arrest and failed to comply with the orders of police at the scene. At one point the official complaint states that three or four cops had to remove her from her vehicle and then she extended her legs in the police vehicle so that the door could not be closed.
You might think that Pearson would be under investigation or some sort of official inquiry by both the school district and the city to see if she should be allowed to continue in her roles.
Instead, apparently, it’s not Pearson who’s the subject of deeper inquires, but the cops who arrested her.
If you find that incredible, join the club. But immediately following Pearson’s arrest on December 19th, the interim Police Monitor, Aeiramique Glass, who answers to Pearson’s board, announced that she was investigating the incident. Of course, the first question the public might be asking is, ‘investigating who for what?’
The Police Monitor is supposed to be a complaint driven process. In fact, the complaint process is so central that it took the previous Monitor two years to so much as come up with a complaint form. So, who filed a complaint here? Did Pearson complain about her arrest? We have no information, but right now we’d have to assume that Glass initiated the process on her own.
That conclusion was backed up today when it was reported that City Attorney Mike Haas ruled on a question of conflict of interest. In his informal ruling, he wrote: “It seems to me that if the focus of any such investigation is the actions of police officers and not the Board Chair, the Independent Monitor has the authority to investigate activities of the Police Department.”
——-
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
SEIU Delenda Est: “perfectingg the art of extortion via ballot initiative.”
California lets interest groups propose measures for the state ballot. Anyone who gathers enough signatures (currently 874,641) can put their hare-brained plans before voters during the next election year.
This year, the big story is the 2026 Billionaire Tax Act, a 5% wealth tax on California’s billionaires. Your views on this will mostly be shaped by whether or not you like taxing the rich, but opponents have argued that it’s an especially poorly written proposal:
- It includes a tax on “unrealized gains”, like a founder’s share of a private company which hasn’t been sold yet. This could be an existential threat tothe Silicon Valley model of building startups that are worth billions on paper before their founders see any cash. Since most billionaires keep most of their wealth in stocks, any wealth tax will need some way to reach these (cf. complaints about the “buy, borrow, die” strategy for avoiding taxation). But there are better ways to do this (for example, taxing at liquidation and treating death as a virtual liquidation event), other wealth tax proposals have included these, and the California proposal doesn’t.
- It appears to value company stakes by voting rights rather than ownership, so a typical founder who maintains control of their company despite dilution might see themselves taxed for more than they have. Garry Tan explains the math here with reference to Google. However, Current Affairs has a good article (?!) that pushes back, saying the proposal exempts public companies like Google. Although private companies would still be affected, this would be so obviously unfair that founders would easily win an exemption based on a provision allowing them to appeal nonsensical results. Still, some might counterobject that proposed legislation is generally supposed to be good, rather than so bad that its victims will easily win on appeal.
- It’s retroactive, applying to billionaires who lived in California in January, even though it won’t come to a vote until November. Proponents argue that this is necessary to prevent billionaire flight; opponents point out that alternatively, billionaires could flee before the tax even passes (as some have already done). One plausible result is that the tax fails (either at the ballot box or the courts), but only after spurring California’s richest taxpayers to flee, leading to a net decrease in revenue.
- Some people propose that it could decrease state revenues overall even if it passed, if it drove out enough billionaires, though others disagree.
Pro-tech-industry newsletter Pirate Wires finds that 20 out of 21 California tech billionaires interviewed were “developing an exit plan” and quotes an insider saying that “if this tax actually passes, I think the technology industry kind of has to leave the state”. Even Gavin Newsom, hardly known for being an anti-tax conservative, has argued that it “makes no sense” and “would be really damaging”.
——-
“SEIU is known in California political circles for pioneering and perfecting the art of extortion via ballot initiative.”
——-
Does Notre Dame deserve an ‘F’ for free expression?
It’s the collective nightmare of all Notre Dame students: a failing grade.
But that’s exactly what our University received last semester on its “free speech report card.” According to the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE), Notre Dame ranks in the bottom 20% of universities nationwide when it comes to issues of free speech and free expression. While we aren’t alone at the bottom — Barnard, Harvard, U Penn, NYU and Columbia received similarly dismal rankings — the shock was enough to make waves in the Notre Dame network, both on and off campus.
The report was so starkly at odds with our self-image that initial responses, including ours, were largely skeptical. For instance, one headline-grabbing finding reports that “24% of Notre Dame students find it acceptable to use violence to stop a disagreeable political speaker.” Given the mild-to-neutral political climate among most students and in most classrooms on campus, many of us found this simply too hard to believe. And if a wild claim like that formed any part of the basis of the failing grade, it almost felt safe to assume bad intentions were somehow skewing the data collection or analysis. “We didn’t opt in to any class with this FIRE organization,” we thought. “Maybe they’re just another political organization trying to grift off widespread ill will toward elite institutions; maybe the rankings are just ragebait.”
But something about these findings struck a nerve. Even if we were being forced to take the course, and even if the grade seemed obviously unfair, we just couldn’t shake the confidence hit of seeing an “F” on a report card with our name on it. We decided we had to investigate. At the time, we, the authors of this piece, were covering the value of free speech and protected disagreement in God and the Good Life; one of us was teaching it, and the other two were taking it. We figured there wasn’t much to lose in doing a deeper dive to see if we could cut through the hype.
Here’s what we found.
The 2026 College Free Speech Rankings
FIRE:
- 68,000+ Students Surveyed
- 250+ Colleges Ranked
The most comprehensive guide to free speech on campus — anywhere
Because a true university education requires freedom of expression
The Problem
Free speech is under continuous threat at many of America’s colleges, pushed aside in favor of politics, comfort, or simply a desire to avoid controversy. As a result, speech codes dictating what may or may not be said, “free speech zones” confining speech to tiny areas of campus, and administrative attempts to punish or repress campus free speech on a case-by-case basis have become all too common.
——
More.
Civics: “No conflict in police monitor investigating arrest of Madison police oversight chair”
Pearson and Grayson were arrested after Grayson refused to move her vehicle — in which Pearson was a passenger — out of a theater’s no-parking area and argued with theater employees, according to police and the Dane County District Attorney’s Office. A source with knowledge of the event has said that the theater was the Majestic, 115 King St.
The criminal complaint against Pearson, who is also a two-term member of the Madison School Board, and Grayson, CEO of Urban Triage, says the two disobeyed police orders and had to be forcibly removed from Grayson’s vehicle and arrested.
Glass and police spokesperson Stephanie Fryer gave no indication Tuesday of when the investigations might be complete.
Glass declined to clarify whether the findings from her investigation will be made public, saying only that “as with all matters under review or independent investigation, public comment or closed-case summaries will be provided at the appropriate time once the process is complete and the case is fully closed.”
Fryer on Tuesday said making the findings of the police investigation public “will depend on the outcome of that review.”
She clarified on Wednesday that “if this review finds we could have served our community better, we won’t hide that. But there has to be a due process that occurs with this review and until it’s finalized we can’t say what will be shared publicly.”
———
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
Civics: Looking Away
A parole officer sent an email: “Agents must not search for violations.” Then two women died.
Now a civil rights lawsuit names the officials who told parole agents to look the other way.
“Now the nation’s first federal voucher program is making an offer that Democratic governors may find hard to refuse”
If governors opt in to the program, tax dollars will go toward private school tuition for children in their states, something many Democrats are uncomfortable with. But if they say no, their states will lose out on a new bottomless bucket of federal cash that could help public school students, too.
Twenty-eight governors have said they will opt in, including all but one Republican (who remains undecided), according to tracking from EdWeek, a news organization that covers education. Two Democratic governors have said their states will participate, and four have said they won’t, but most have ducked the question, as pressure rises from all sides.
“What makes the program tricky is that it blurs the party lines on school choice. It’s not a traditional voucher,” said Michelle Dimino, director of education at Third Way, a centrist Democratic think tank, who is urging states to opt in. “But opposition to any school choice policy is deeply ingrained for many Democrats.”
The Closure of Four Chicago Catholic Grade Schools
The closing of four Catholic elementary schools in Chicago, Saints Bruno & Richard, Saint Jerome, Saint Stanislaus Kostka Academy, and Saint Francis Borgia looks at first glance like a familiar story: Declining enrollment, rising costs, and another set of urban parish schools unable to make the numbers work. But beneath the surface sits a more complicated policy question. If these schools deliver solid academic outcomes at substantially lower per-pupil cost than the public system, should policymakers care? And if so, what tools, such as tax-credit scholarships, vouchers, or federal donor credits are appropriate to keep such schools alive?
On January 16th the Chicago Tribune reported on the closing of those schools. There was only talk of the money-raising efforts of those schools falling short of the funds needed to survive. On January 27th the Chicago Tribune reported on the Big Beautiful Bill’s federal educational voucher program and whether Governor JB Pritzker would opt into it. Even though the reports were only 24 hours apart, there was no reporting on the cross-over of the two reports. Does the Tribune have any editors left?
This is not merely a parochial matter. It is a test case in how cities manage educational capacity, parental choice and taxpayer dollars.
Catholic urban schools have long punched above their financial weight. Their model is lean: Smaller administrations, lower teacher salaries and pensions than unionized public systems, parish and donor support, and tighter community expectations around behavior and attendance. Tuition at the four closing Chicago schools generally ran in the $6,000–$7,500 range, often discounted through aid. Even after accounting for parish subsidy and fundraising, credible estimates put their true operating cost around $9,000–$11,000 per student.
Back to the Suburbs: Chicago Edition
Downtown fell 40%. The suburbs gained 45%. The gap is still widening.
Home prices have soared since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, but a rising tide has not lifted all boats: home prices in the suburbs and exurbs have risen far faster than city cores. Of the 50 largest U.S. metros, Chicago’s 30-point urban-exurban gap is the third widest in the country (after New York City and San Francisco). The map below shows the cumulative change in home prices for each ZIP code in and around Chicago since January 2020.
Civics: Welfare Use by Immigrants and the U.S.-Born, 2024
By Steven A. Camarota and Karen Zeigler:
Using the 2024 Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP), this analysis follows the Census Bureau’s standard definition of welfare and reports use of means-tested anti-poverty programs by households headed by immigrants and the U.S.-born. We exclude social insurance programs like Social Security and Medicare, which individuals pay in to and are not means-tested. The findings show that households headed by immigrants, also called the “foreign-born”, are significantly more likely to receive benefits than households headed by the U.S.-born. The ability of low-income immigrants, including illegal immigrants, to receive benefits on behalf of U.S.-born citizen children is a key reason restrictions on welfare use for new legal immigrants, and illegal immigrants, are relatively ineffective. If we want immigrants to use less welfare in the future, then reducing illegal immigration and changing the selection criteria for legal immigrants to emphasize skills should be considered.
Among the findings:
- The 2024 SIPP indicates that 53 percent of households headed by immigrants — naturalized citizens, legal residents, and illegal immigrants — used one or more major welfare programs. This compares to 37 percent for U.S.-born households.
- The rate is 59 percent for non-citizen households (e.g. green card holders and illegal immigrants).
- Compared to households headed by the U.S.-born, immigrant-headed households have especially high use of food programs (35 percent vs. 22 percent for the U.S.-born), Medicaid (39 percent vs. 27 percent for the U.S.-born), and the Earned Income Tax Credit (15 percent vs. 10 percent for the U.S.-born).
- Our best estimate is that 51 percent of households headed by legal immigrants use at least one major welfare program. Among illegal immigrants, also called the undocumented, we estimate the rate is 61 percent. We have no evidence that this is due to fraud.
Teacher-Led or Student-Centered? What the Research Says About Equity
Student-centered learning is often associated with greater equity in the classroom. But does it actually reduce achievement gaps? A new study by Zhu et al. (2026)1 suggests the answer may be more complicated than many educators assume.
To investigate this question, Zhu and colleagues analyzed how different teaching approaches related to equity in real classrooms. They distinguished between two broad categories of instruction: (i) teacher-led instruction (e.g., explicit, direct teaching); and (ii) student-centered learning (e.g., discovery, inquiry-based, problem-based approaches).
Using a large, nationally representative dataset of U.S. eighth-grade mathematics students, the researchers examined how each approach related to achievement across socioeconomic groups. Both teacher-led and student-centered practices were used at similar rates across schools serving different socioeconomic communities, allowing meaningful comparison.
Teacher-led instruction, characterized by clear explanations, structured support, and guided practice, was associated with significantly stronger mathematics performance for students from lower socioeconomic backgrounds. It was also the only approach that reduced the achievement gap between low- and middle-SES students. Student-centered approaches, characterized by inquiry, exploration, and greater student autonomy, were not associated with reductions in the achievement gap.
The study raises an important question: Why might student-centered practices, which are often assumed to promote equity, be less effective in shrinking achievement gaps? To illustrate why they can sometimes produce less equitable outcomes, consider the following scenario:
“While enrollment has declined 24% since 2016, staffing has declined 14.7%”
Since the 2016-17 school year, enrollment in Marblehead Public Schools has declined from 3,144 students to a projected 2,389 students this year — a 24% decrease. This shift reflects long-term demographic changes in our town and is not indicative of a decline in school quality. Communities across Massachusetts and the nation are experiencing similar enrollment declines, driven by lower birth rates and aging populations. Public school participation in Marblehead has remained steady at 76% to 79% of school-aged residents for nearly a decade; the reality is simply that many households whose children once filled our classrooms have aged out. Since 2016, the share of residents age 65 and older has risen from 17.9% to 22.6% — meaning roughly 1,100 more Marblehead residents are now over age 65 than in 2016.
Proactive rightsizing: The district has not been idle in the face of these shifts. The consolidation of Bell, Coffin and Gerry into the Brown School was a significant, multiyear structural change driven by projected declines in enrollment. By reducing our building footprint, we eliminated the overhead of maintaining aging facilities and redundant programs. This was a proactive rightsizing of our infrastructure designed specifically to address the demographic shifts we are seeing today.
The staffing “delta”: While enrollment has declined 24% since 2016, staffing has declined 14.7%. That 9% gap understandably raises questions. Two factors explain most of it:
——-
More.
Since 2006, WI has lost more than 83,000 students. Some of it is demographic reality. Some of it is parents fed up with failing schools.
——-
Locally, Madison taxpayers are $pending more amidst flat to declining enrollment:
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
24 Hours: Diversity Statements, Sausage Making and UW Madison’s Overton Window
I often find interesting talks when occasionally visiting today.wisc.edu. However, awareness of John Sailer’s March 4, 2026 talk arrived via email, with no presence – as far as I could find – on today.wisc.edu (search results for Sailer).
I did observe a related notice displayed on 5 March 2026: “Diversity/Equity/Inclusivity Statements for the Academic Job Market”, which further links to the Center for the Integration of Research, Teaching and Learning, or CIRTL.

Terms:
Scholar-activist pipeline | Diversity Statements | Cluster Hiring | Mellon Foundation | academic freedom | ideological filtering | NIH First | Career Investment
Screenshots:


K-12 Related Links:
“An emphasis on adult employment”“The grant made me do it”: Small Learning Communities
Griffin and Bezos Fund Personalized Math in Miami Public Schools
Billionaire Ken Griffin is bringing personalized math instruction to Miami-Dade County public schools as the recent transplant looks to bolster education outcomes in the region.
Griffin and the Bezos Family Foundation — whose chair, Mike Bezos, and board member Jeff Bezos have also relocated to Miami — put up $7 million to fund a three-year pilot by New Jersey-based New Classrooms.
Generous school spending doesn’t always deliver results

The growing progressive interest in exotic new tax-policy ideas — like Bernie Sanders and Ro Khanna saying they can raise trillions in revenue from a base of around 1,000 billionaires — shows a left that has lost faith in the idea of asking Americans to pay higher taxes in exchange for more and better public services.
And whatever you think of the Sanders/Khanna proposal,1 it’s important to understand that this kind of plan doesn’t scale well to small states or to cities and counties since it can be relatively easy for people to leave to avoid the taxes.
So, especially when it comes to local services, you really have to ask questions like “Can we make people feel that it’s worth paying more for this?” and “Can we get more value for the money that we are already spending?” Unlike with the federal government, where DOGE failed in part because it was based on wildly false premises, local governments actually spend a huge share of their budget on direct provision of labor-intensive public services.
The most expensive of these line items is public school systems.
Education spending presents us with something of a paradox. We know from small-scale studies that marginal increases in school spending produce positive results for children. In particular, fairly boring things like improving school HVAC systems are effective at promoting student learning, especially in low-socioeconomic-status schools.
——-
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
Civics: “and he was set free”
The courtroom had been packed all day but as case after case was handled, ours was the last one—now it was just the judge, court reporter, bailiff, the defendant, his lawyer, the Commonwealth attorney, and I.
The arresting officer wasn’t in the room. The other victim and her husband had been given a new court date and sent home.
I adjusted my baby against my chest and looked at her as she repeated the question: Do you see the man you reported to police in this room today?
Why was she doing this? What was she doing?
I was sweating in my oversized cashmere nursing sweater and I felt prickles down my back. Everyone was staring at me. I’m not a lawyer. She asked me a question… and she was “on my side” so I should answer it, right?
I adjusted my baby again to give myself a free hand—and I pointed to him.
——
@SteveDescano we don’t need you to feel sorry for us – we need you to stop letting violent criminals walk free.
Civics: Loopholes, delays, poor enforcement plague Mass. public records law
“I’ve gotten nothing [that would] enable the transparency that is the point of the public records law,” McCarter said. “They don’t even pretend to comply, never mind do anything that would allow public oversight.”
McCarter is hardly alone in his frustrations.
For nearly two centuries, Massachusetts law has guaranteed government records are open and accessible. But a Globe review has found the state’s public records law has often proved to be a promise written in sand.
“Massachusetts is one of the more secretive states. The governments have learned to game the system, and the law has little enforcement,” said David Cuillier, the director of the Freedom of Information Project at the Brechner Center for the Advancement of the First Amendment at the University of Florida.
In Massachusetts, the state law’s deadlines for fulfilling records requests can be ignored, workers can conspire to overestimate costs, elected officials can spend years fighting requests in court, or not bother releasing records at all. No one tracks whether local governments like cities and school districts follow the law; state agencies self-report requests, but not the reasons why they refuse them.
“Interestingly, the majority of voters in a new Harvard/Harris poll believe teachers’ unions shouldn’t be involved in politics”
Can school board reform slate win in age of culture wars?
- A four-candidate reform slate is running for the Wauwatosa School Board.
- The slate is focused on financial accountability, teacher retention, and academic performance.
- The candidates point to falling student enrollment and rising staff numbers as an unsustainable budget issue.
- If successful, the slate’s victory could signal a voter preference for governance over partisan culture war issues.
Chris Merker ran for school board last year and lost by a slim margin. This year, he thinks he can not only win a seat himself but help elect a four-candidate reform team to secure a governing majority on the Wauwatosa School Board.
A federal education policy analyst by day, I’m watching this race closely because it tests a national question in miniature: Can a slate focused on the nuts-and-bolts of good governance and financial accountability win in partisan times?
Civics: Who’s That Source?
Why this feature now? A large portion of what’s consumed as journalism is a pure partisan product, with ex-politicians reading out “news” stuffed with “facts” produced by de facto political action committees. Worse, the habit of relying on paid political mouthpieces comes at a time when stylistically, editors have less shame about presenting an “Experts Say” headline as a news event, when it’s really an op-ed or de facto advertisement. Some sites are shameless enough to shove “Experts Say” headlines into print without telling you which experts — a bottom-of-barrel sourcing technique we call “The Full Windbag.”
My Criticism of the Ivy League Isn’t Hypocrisy
When politicians who graduated from Ivy League schools speak out against them, they’re often called hypocrites. Think of Ted Cruz, Josh Hawley, JD Vance, Ron DeSantis and Elise Stefanik. In 2024, Rob McCarron, who heads the Association of Independent Colleges and Universities in Massachusetts, called it “unfortunate, and ironic, when individuals who have benefited greatly from a college education, and continue to reap those benefits, are the most vocal critics of higher education.”
“Toxic Empathy”: When ‘be nice’ becomes the whole ethic, we’re in trouble
The appeal to pity is the modern left’s favorite fallacy.
In logic, it is called argumentum ad misericordiam. Instead of showing that a policy is just or true, the speaker points to suffering and insists compassion requires agreement. It works because it weaponizes one of the strongest moral instincts in the American people: mercy.
Deep empathy does not sneer at suffering. It refuses to treat feeling as the foundation of ethics.
The person making the appeal to pity is not merely expressing concern. He is using your compassion to secure special treatment, expanded power, or ideological conformity. And because America remains culturally shaped by Christianity — a faith that commands love of neighbor — the tactic often succeeds.
Allie Beth Stuckey and Joe Rigney have warned about what they call the weaponization of empathy. Empathy, properly understood, is the act of feeling the pain of another. It differs from sympathy, which acknowledges suffering without necessarily taking it on. Empathy attempts to enter another person’s emotional state.
But empathy rests on feeling, and feelings fluctuate. They can be misinformed. They can be manipulated. They can even be built on fiction.
Civics: Propaganda and the legacy media
I know it’s rude to mention it, but @TheAtlantic is run by Jeffrey Goldberg, the media figure most responsible for selling Americans the key Iraq War lie that Saddam was allied with Al Qaeda, and who joined the IDF (but never the US military) to work as an IDF prison guard. ii
Uta Frith: why I no longer think autism is a spectrum
“I feel more and more under pressure to really think about this problem,” says Dame Uta Frith, referring to the exponential rise in the number of young people being diagnosed with autism.
According to the Institute for Fiscal Studies, the number of children with EHCPs for autism spectrum disorder almost tripled between 2015 and 2025, accounting for 40 per cent of the total increase in EHCPs.
It’s a rise that has placed unprecedented strain on schools – and led the government to include autism as a focus of an independent review into rising demand for services for mental health, ADHD and autism, which is set to report later this year.
That review is welcomed by Frith, who is emeritus professor in cognitive development at the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London (UCL), and the person who pioneered much of the research that underpins our current understanding of autism.
She is, she says, “very happy to see that some action is being taken to understand why there has been such a dramatic increase in ASD diagnosis and why we have such long waiting lists. The current situation is dire, and something must be done.”
——
K-12 Tax & $pending Climate: Minnesota Promise grants gave millions to small businesses. Here’s what happened when we vetted the recipients
But state records show the company has billed Medicaid nearly $4 million since 2023, including through a state housing program shut down last fall amid fraud concerns.
By phone, the company’s owner told 5 INVESTIGATES that when he applied, his business’ revenue was under the $750,000 limit to qualify.
GOP State Representative Nolan West called the findings “inexcusable.”
“If you just have to fill out some paperwork and get five grand, I think a lot of people would take that deal,” he said. “It’s free money. Just file the paperwork.”
Another business, B&M Vital Homecare, received $47,000 — nearly the maximum grant amount — even though the state revoked its license two years ago for what officials described as a “serious issue” affecting client health and safety.
Politics, Security and Taxpayers
California taxpayers have been paying for former Vice President Kamala Harris’ security detail as she travels out of state and, in some cases, out of the country to promote her book.
Multiple sources who were unauthorized to speak publicly about security matters told KCRA 3 that dozens of California Highway Patrol officers have been traveling with her for all of the former vice president’s book tour appearances. State officials will not say exactly how many officers are assigned to her, how long the arrangement will last and how much taxpayer money is being used.
The Ivies Are Having Second Thoughts About Investing in Private Equity
Private equity is on academic probation.
Princeton University is lowering expectations for its endowment’s returns because its private-capital investments have disappointed. Yale trimmed its portfolio of leveraged buyouts for the first time in a decade. Harvard says cashing out of some private-market investments early is now part of a long-term strategy.
Private equity has counted America’s wealthiest universities among its largest and most-loyal clients since the industry’s formative years. But the market for private-company investments has turned more crowded, and returns now struggle to match broader stock-market benchmarks such as the S&P 500.
University endowments grew to lean on the once-juicy returns of private equity to cover a larger slice of their overall budget. That strategy faltered when the long lockup investments returned an annualized 7.4% in the three years ended June 30, according to Cambridge Associates—much of it paper gains. Over that same period, the S&P 500 rose 19.7% a year.
“independent charter schools have the highest median performance relative to demographic expectations of any school sector”
We also look at Wisconsin’s largest school choice program–open enrollment. Here, you see the marketplace working as families move to school districts with better academic outcomes and graduation rates.
WILL’s Apples to Apples report provides a rigorous, side-by-side comparison of academic performance across Wisconsin’s public, charter, and private choice schools. Because student achievement is strongly shaped by factors such as income, disability status, and English learner status, simple comparisons of raw test scores can be misleading.
This report addresses that problem by applying a consistent analytical framework that adjusts for key student and school characteristics, allowing for fairer comparisons across sectors. The 2026 edition uses the most recent data from Wisconsin DPI’s 2024–25 report cards and reflects important methodological updates, including the addition of disability rates as a control variable directly for the first time.
———
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
Understanding High Schools’ Effects on Longer-Term Outcomes
Preeya P. Mbekeani, John P. Papay, Ann Mantil & Richard J. Murnane:
Improving education and labor market outcomes for low-income students is critical for advancing socioeconomic mobility in the United States. We use longitudinal data on five cohorts of 9th grade students to explore how Massachusetts public high schools affect the longer-term outcomes of students, with a special focus on students from low-income families. Using detailed administrative and student survey data, we estimate school value-added impacts on college outcomes and earnings. Observationally similar students who attend a school at the 80th percentile of the value-added distribution instead of a school at the 20th percentile are 11% more likely to enroll in college, are 31% more likely to graduate from a four-year college, and earn 25% (or $10,500) more annually at age 30. On average, schools that improve students’ longer-run outcomes the most are those that improve their 10th grade test scores and increase their college plans the most.
———
Madison’s English 10.
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
“Schools have become laboratories for esoteric ideological projects, not centers of learning”
Far too many children are still assigned to substandard schools, and too many remain unable to read or do math at grade level. Meanwhile, educators and policymakers seem preoccupied with nonsense like helping students “transition” behind their parents’ backs or indoctrinating impressionable youngsters with social-justice poppycock to promote trendy political causes. American kids are outperformed by their foreign peers on international exams while we have to concern ourselves with whether school libraries make sexually explicit texts available to third-graders.
For a growing number of people in charge of the public education establishment, making sure that boys can play on girls’ sports teams has become more important than making sure students are acquiring basic academic skills that will enable them to learn a trade, complete college, become productive adults.
One of the few bright spots in our education system has been selective-enrollment public high schools, which use standardized tests and other objective measures to determine admissions. Examples include Boston Latin School in Massachusetts, Stuyvesant High School in Manhattan and Thomas Jefferson High School in Alexandria, Va., all of which boast long and proven records of providing a rigorous education for students from all backgrounds. Yet even this successful model is increasingly under attack, and its future is uncertain.
A new study from the Manhattan Institute details efforts in Chicago to eliminate selective public high schools. Much of the Chicago public school system is in shambles. Wirepoints, a government watchdog group, reported last year that the Chicago Public School system operated 53 schools in 2024 where not a single student tested proficient in math, and 17 schools in which no student tested proficient in reading. Mayor Brandon Johnson and other Democrats blame these outcomes on a lack of resources, but spending per pupil has almost doubled since 2017, and teacher pay in the Windy City is among the highest in the nation for large school districts after adjusting for cost of living.
——-
I believe the reason black and Latino kids do so much worse than white and Asian kids is that large urban public school districts that educate most of these students are incredibly wasteful with resources and adhere to politically progressive methods of teaching that stifle talented students and don’t help low performers. But it’s not a high bar to be better than schools in Central America or Africa.
———
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
Notes on the Mellon Grant Industrial Complex
For Alexander’s courage, she was paid $2.2 million in combined compensation in 2024. One reason it’s hard to take this mumbo jumbo seriously is that supporters of elite “social justice” do things like call the fabulously rich leader of a billion-dollar philanthropy “courageous.”
more.
This is a hilarious illustration of Mellon’s power: guy has criticisms of my article (fair!) but admits donors having monopoly power is concerning. Then his friends yell at him, he apologizes for his white privilege, says I’m an enemy of racial justice, and deletes the article.
Universities, budgets and endowments
US university endowments have recorded their fastest spending growth since the global financial crisis as federal funding cuts and rising operating costs squeeze campus budgets.
A study of 657 institutions by the National Association of College and University Business Officers (Nacubo) with Commonfund showed their endowment withdrawals rose 11 per cent year on year in the 12 months to June 2025 — the sharpest increase since 2010.
The surge came as endowments funded an average of 15.2 per cent of universities’ operating expenses last year, up from 10.9 per cent in 2023.
——-
Florida public universities to pause hiring new H-1B workers until end of the year
The moratorium follows Gov. Ron DeSantis’ criticisms of the H-1B program last fall. He pointed to employers who use the program to hire foreign workers at lower wages than U.S.-born workers.
Connor O’Brien, a fellow at the non-partisan think tank Institute for Progress (IFP), said he recognized the concerns, but worried the hiring freeze goes too far.
“The H-1B has long been abused by IT outsourcing firms sponsoring middle skill workers for underwhelming pay,” said O’Brien, “Unfortunately, the proposal, as currently written, would go much further than trimming back the questionable uses of the visa at state schools.”
O’Brien pushed for an exception for researchers, scientists and physicians, pointing out how a ban could affect medical institutions like University of Florida Health.
Advocating Open Enrollment
A report from the nonpartisan California Legislative Analyst’s Office and a 2023 Reason Foundation study both found that the competitive effects of open enrollment also encourage public school districts to improve. In fact, when interviewed for a 2023 EdChoice report, public school district administrators in Arizona, North Carolina, Indiana, and Florida stated that open enrollment encouraged them to innovate by creating new programs and improving existing programs to better attract and retain students.
Research also shows that K–12 open enrollment is widely used and supported. Reason Foundation’s K–12 Open Enrollment by the Numbers: 2025 study found 22% of Delaware students and 28% of Colorado students in public schools used open enrollment to transfer and attend schools that were the right fit for them. Furthermore, according to a 2025 national poll by EdChoice, open enrollment is supported by 75% of school parents across party lines—80% of Republicans, 75% of Democrats, and 74% of independents—in favor of allowing families to attend public schools outside their assigned district’s boundaries. This bipartisan support led, in part, to open enrollment legislation being passed and signed into law in Idaho, Montana, and West Virginia (2023) and Nevada (2025).
Yet, as explained in this year’s edition of Public Schools Without Boundaries, Maryland is one of only four states that deprives students of any cross- or within-district open enrollment options, scoring a 0 out of Reason’s 100-point best practices criteria (an “F” letter grade). This leaves significant room for policy improvements across all seven key metrics that the study evaluates.
On chief Cassondra Curiel
United Educators of San Francisco President Cassondra Curiel was beaming Friday — not because it was 70 degrees in February, but because her union’s new contract had officially been ratified by 92% of teachers.
Following a four-day strike earlier this month, Curiel’s 6,000-member union received its chief demand from San Francisco Unified School District: fully funded healthcare for dependents. It was enough, the union leader said, for some of her members to start planning on conceiving children.
“It’s inspiring conversations amongst members who have been holding off or uncertain financially,” Curiel said. “That’s really a great thing for San Francisco, because it’s not just techies who live here.”
But the ripple effects of the strike carry on. SFUSD has said the terms of its new contract, which include raises of between 5% and 8.5% over the next two years, will cost $183 million(opens in new tab) through the 2027-28 school year. The district is now planning to issue preliminary lay-off notices for 42 positions, including instructional aides and art teachers.
Why China’s women are having fewer babies
Eleanor Olcott, Tina Hu and Haohsiang Ko:
In 2015, China welcomed almost 16.5mn babies. A decade later, that figure has more than halved to just under 8mn — a striking example of a demographic crisis that is poised to have long-term economic and societal consequences in the world’s second-largest economy.
While China is not alone in grappling with an ageing population, particularly in east Asia, the pace of ageing has been accelerated by the legacy of the “one-child” policy, a weak economy and a growing divide between young men and women’s prospects and intentions.
The “shockingly low number” of new births meant that the “total population will shrink much faster and will become more dominated by the elderly than even in recent pessimistic forecasts”, said Ernan Cui, an expert in Chinese demographics at the consultancy Gavekal Research.
What does an unconstitutional “gender support policy” look like? Below is one from Madison, Wis.
Note that the plan tells teachers to actively deceive parents by referring to students one way in school & another way in front of family.


WILL:
“The Supreme Court reinforced that parents have enforceable rights to be involved in major decisions affecting their children’s health and wellbeing. Because of this clarification, WILL is providing school districts with guidance on how to respect parents’ rights and reduce the risk of legal challenges. The message is clear: school policies that allow students to socially transition without parental consent risk expensive lawsuits and significant liability.”
———
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
K-12 Tax & $pending Climate: Administrative Salaries and Lawfare
District admins in the districts currently suing over a lack of funds all make nearly $150K per year-about 3X the median income for a US worker. 3 pay their admins more than $200K in taxpayer money/year. Yet they have the audacity to demand more from taxpayers around the state?
——
Lawfare seeks to grow Madison’s $26k/student taxpayer spending
$pending on Bricks & Mortar vs Academics
“MPS is operating 25 more schools than it needs. Schools operating at 50-60% capacity still require full heating, maintenance, and administrative costs. Every dollar spent maintaining underutilized infrastructure is a dollar not invested in” academics.
Nearly half of Wisconsin’s lowest performing schools are on Milwaukee’s north side
———-
Madison, too is $pending heavily on bricks and mortar despite flat to declining enrollment.
Canadian students’ math scores are falling. What B.C. schools and parents can do about it
Her call to action is echoed, on a much larger scale, by math and education experts alarmed over Canadian students’ declining math performance on global tests. A recent report from the C.D. Howe Institute called it an “urgent national concern” that requires immediate action by provincial governments.
The report highlighted Canada’s performance over the past decade on two international assessments.
Results from the 2023 Trends In International Mathematics and Science Study showed Canadian Grade 4 students scored well below their peers from the U.S., England and Germany in most benchmark levels.
Canada had a better showing on the Programme for International Student Assessment, which assesses, in part, the math skills of 15-year-olds in 81 countries. In 2022, Canada ranked ninth.
——-
2014: 21% of University of Wisconsin System Freshman Require Remedial Math
How One Woman Rewrote Math in Corvallis
Singapore Math
Discovery Math
Math Forum 2007
K-12 tax & $pending climate: Washington doubled spending over 10 years. Every major metric got worse, but Olympia still wants more –
Ten years ago, I wasn’t highly skeptical of state spending. I’m not so sure anymore.
I covered Olympia long enough to know that most of the people there genuinely want to help. The problems they’re wrestling with — homelessness, addiction, education, housing — are real and genuinely hard. A pandemic hit at the start of the decade and scrambled everything. The population grew. I get it.
But at some point, the results have to show up.
WA spending doubled. The numbers don’t lie
Washington spending has more than doubled in the past 10 years, from $81.8 billion to $173.5 billion. Some of that is inflation, and our population grew, too. Fair points. But even after you account for both, we’re spending about 40% more per person in real dollars than we were a decade ago.
And I keep waiting for the results to show up.
For that kind of money, it’s fair to expect something. Better schools. Less homelessness. Fewer people dying of overdoses. Easier commutes. Instead, just about every one of those metrics went in the wrong direction.
How Dartmouth College went all-in on AI
Dartmouth leaders are not mandating the use of AI, yetcritics on campus say they’ve had little opportunity to adapt to what they see as a massive change to how the college works. At stake, they say, is the tight-knit academic culture Dartmouth has nurtured in rural New Hampshire over nearly three centuries as a school that focuses on the liberal arts, with a small student body and deeply personal style of instruction. It’s the only Ivy League institution with “college,” rather than “university,” in its name.
“There is no escaping [AI], and they have to figure out how to use it wisely,” said Charles Fadel, the Boston-based founder of the nonprofit Center for Curriculum Redesign. “The hard part is to accept that you are going to lose something.”
The recent efforts at Dartmouth — touted as the birthplace of AI, thanks to a seminal 1956 research conference on campus — largely began with James Dobson. The English professor was appointed as the special adviser to the provost on AI and drafted a reportlast year on the adoption of the technology. It recommended investing in data infrastructure and a partnership with a company like Anthropic — creator of the chatbot Claude — that would gradually integrate the tech into most facets of campus life.
The report marked how far Dartmouth has to go. Dobson’s own department has integrated AI in most first-year writing courses, where students sometimes compare close readings of scholarly articles to artificial intelligence-generated summaries. But he said the majority of faculty still ban the use of generative AI in their syllabuses, a “totally unenforceable” measure, he added. And a survey showed that over half of participating professors had not changed their assessments to reflect AI as of last summer.
Understanding High Schools’ Effects on Longer-Term Outcomes
Preeya P. Mbekeani, John P. Papay, Ann Mantil & Richard J. Murnane:
Improving education and labor market outcomes for low-income students is critical for advancing socioeconomic mobility in the United States. We use longitudinal data on five cohorts of 9th grade students to explore how Massachusetts public high schools affect the longer-term outcomes of students, with a special focus on students from low-income families. Using detailed administrative and student survey data, we estimate school value-added impacts on college outcomes and earnings. Observationally similar students who attend a school at the 80th percentile of the value-added distribution instead of a school at the 20th percentile are 11% more likely to enroll in college, are 31% more likely to graduate from a four-year college, and earn 25% (or $10,500) more annually at age 30. On average, schools that improve students’ longer-run outcomes the most are those that improve their 10th grade test scores and increase their college plans the most.
———
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
“while keeping per-capita spending increases below the rate of inflation”
The totality of these policies has proved poisonous to California citizens. Since Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger left office in 2011, California’s budget has grown two and a half times (opens in new tab) to almost $300 billion. But no rider of BART, parent of a California student, or renter or prospective homebuyer in the state would say their life is two and a half times better.
Since taking office in 2019, Newsom has boosted staffing in the executive branch by 20% (opens in new tab) and added $11 billion to annual spending on compensation and benefits. When faced with recent deficits, he tapped budget reserves rather than freeze hiring or compensation. This isn’t incompetence — it’s political self-preservation.
Meanwhile, Texas and Florida have absorbed massive population growth (opens in new tab) while keeping per-capita spending increases below the rate of inflation. The difference isn’t the cost of living; it’s the cost of elected officials in California giving in to public employee unions. Breaking that cycle requires citizen action. Real change will come only when voters reward politicians who serve them instead of special interests.
As Newsom eyes the White House in 2028, he faces a question that could define his candidacy: Should he roll over and endorse two new taxes and even higher spending? Or does he have the will to challenge the unions that have funded his campaigns (opens in new tab)?
“Since Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger left office in 2011, California’s budget has grown two and a half times to almost $300 billion…
Princeton University cuts expectation for endowment returns
Princeton University has cut the long-term return assumption on its $36bn endowment, as heavy exposure to crowded private equity investments weighs on its ability to repeat its past performance.
Christopher Eisgruber, Princeton’s president, said in his annual state of the University letter on Monday that “changing market fundamentals”, driven by excess capital in limited investment opportunities, would cause a persistent decline in long-term returns. The endowment has lowered its return expectations from 10.2 per cent to 8 per cent, though even the lower assumption “might be considered aggressive”.
The reduction could translate into $11bn less in endowment assets over the next decade, a figure exceeding the proceeds of the university’s past two big fundraising campaigns combined. As a result, Princeton had sought 5 to 7 per cent spending cuts across the university over the past 12 months, said Eisgruber, adding that the long-term decline in endowment return would require “more targeted, and in some cases deeper, reductions over a multiyear period”.
Princeton’s move underscores the challenges facing the endowment investment model, which relies heavily on illiquid but historically lucrative private assets. Higher interest rates have slowed exits in the short term by curbing initial public offerings and acquisitions, while an oversupply of capital has intensified competition for deals, compressing returns over the longer run.
The Waterpark Department
The Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction is returning to the Wisconsin Dells for its 11th annual WISEdata Conference on March 18 and 19. This gathering of school administrators and data coordinators comes as the agency tells state lawmakers in Madison that it is facing a dire fiscal crisis that could lead to staff layoffs.
The conference serves as a technical training site for DPI staff and the local school district employees who manage state reporting systems. While the agency calls the event a “community” effort, the choice of venue follows a pattern of spending that has already frustrated the Legislature. The DPI selected the same resort, Chula Vista, where it spent $368,885 on a four-day workshop in June of 2024.
For this month’s event, the DPI says the costs of rooms and travel are not covered by the state. However, that does not mean the public is off the hook. Local school districts often pick up the tab for resort stays using property tax revenue or federal grants.
——-
Per-pupil spending is at its highest level since 2000 even after adjusting for inflation, according to data from DPI.
“can you train a model on Apple’s Neural Engine?”
Apple doesn’t want you to know the answer. They don’t publish the ANE’s ISA. They don’t document its internal architecture. They don’t even give you a way to program it directly — everything goes through CoreML, which adds layers of abstraction, optimization passes, and overhead that make it nearly impossible to understand what the hardware is actually doing.
So we reverse-engineered it.
Over several days, we mapped the entire software stack from CoreML down to the IOKit kernel driver, discovered how to compile and execute programs on the ANE without CoreML, cracked the binary format, measured the true peak performance (spoiler: Apple’s “38 TOPS” number is misleading), and ultimately got a neural network training on a chip designed exclusively for inference.
This is Part 1 of a three-part series. Here we cover the reverse engineering — how we peeled back the layers to understand what the M4 Neural Engine actually is and how to talk to it directly.
Time for UW-Madison to do away with ethnic studies requirement
Time can be better spent on other things like AI
Here’s a question I hope somebody asks anyone who applies to be the next chancellor of the University of Wisconsin-Madison: Why in the world in 2026 should we continue to have an ethnic studies requirement for all undergrads?
Here’s another one: Do you even know what it is and what it entails?
The Property Tax Revolt
Riley Judd: in
In Florida, meanwhile, the effort to eliminate property taxes is being led by Governor Ron DeSantis (R), who pushed to end property taxes during the 2025 legislative session. Although lawmakers stopped short of doing so, they did establish a bipartisan committee to study the issue.
That committee has now approved a slate of property tax reform proposals—ranging from expanding homestead exemptions to eliminating nonschool homestead property taxes—that would go to voters in November if the proposals pass during the upcoming legislative session. Three measures are up for final consideration in the Florida House of Representatives, but none has companion legislation in the state Senate, putting their prospects for enactment this session in question.
Many of the bills have generated pushback from local leaders. Fire departments and emergency services are especially concerned because some proposals do not shield them from the impact of property tax cuts—unlike law enforcement and schools—leaving their budgets vulnerable.
Amid legislative uncertainty and concerns from local officials, property tax relief remains a priority for the Florida governor. His proposed budget includes $300 million to offset the effects of homestead property tax cuts for fiscally constrained counties. DeSantis has also said he would call a special session this year if lawmakers don’t put a constitutional amendment to eliminate property taxes on the November 2026 ballot during their regular session.
——-
As families are rocked with property tax increases… in large part due to @GovEvers 400 year increase… you have to start asking…….where is the money being spent?
———
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
“the mayor responsible for probably consigning Oakland to bankruptcy via illegal activism was awarded a sinecure as a lecturer at UC Berkeley’s Goldman School of Public Policy”
It’s very on brand for California that one of the factors pushing Oakland towards a possible bankruptcy is environmental activists pushing the city to illegally renege on a port contract
Taxpayers are now on the hook for up to $654 million, before interest
Outsourcing Our Children
Identifying the victims of career-oriented feminism.
This social experiment is, of course, the mother-child separation required by the feminist notion that a woman’s personal fulfillment requires her energetic participation in the workplace. Eberstadt calls defenders of this conceit “separationists”: those who believe that women’s freedom to work in the paid marketplace justifies separation from their children, and who refuse to consider whether the children and adolescents left behind by the adult exodus have suffered. She challenges a society, which only seems concerned with making it easier and cheaper for women to “combine work and family,” to consider how small children actually experience being in daycare all day. She makes the very sensible point that the daycare debate is never about what it feels like for the infant and children in day care, but always about what the outcomes are in terms of personality development and cognitive ability. “The daycare proof,” separationists believe, “is in the achievement pudding.” Separationists, however, are often not around children, who, in their lives, have been made “someone else’s problem.”
* * *
We have long known that being in day-care centers increases illnesses among children, but Eberstadt analyzes this problem from the child’s, not the adult’s, perspective. What must it be like for a sick child, dosed with Tylenol to disguise an illness before being dropped off at the center? “Anyone actually charged with the care of little children,” she observes, “knows that a sick baby or toddler is a uniquely pitiful thing, in part because such a child is too young to understand why.” Through the eyes of children, Eberstadt details the numerous areas in which their lives have worsened during the period when increasing numbers of mothers left the home, and she establishes the connections between parental absence and children’s present afflictions.
Parental absence, she demonstrates, is implicated in the savage behaviors of serial and teenaged killers and in increased feral behaviors ranging from elementary school violence to suicides (those born in the 1970s and 1980s are three to four times more likely to commit suicide than people of a comparable age who were born at mid-century). Parental absence is also implicated in the obesity epidemic among children, which occurred when adults were no longer around to police children’s eating habits and when shorter periods of breast-feeding by working mothers deprived babies of the protection against obesity that breast-feeding affords. She connects parental absence to the explosion in the number of children diagnosed with mental disorders: depression rates in children have risen tenfold since the end of World War II and children in single-parent families are two to three times more likely to have emotional and behavioral problems. And parental absence is again implicated in the staggering increase in the number of children and teenagers diagnosed with attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, oppositional defiance disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and autism.
We can’t let the Kamloops child burial hoax continue unchecked
Nearly five years later, not one grave has been proven — but millions in taxpayer dollars have vanished into what increasingly looks like a national hoax.
The hoax goes on.
It’s been nearly five years since the bombshell revelation was released that the graves of 215 children had been found at the site of the former Kamloops Residential School. Since then, the Tk’emlups te Secwepemc First Nation was given over $12 million to exhume and identify the remains. While the band made the money vanish, it didn’t move a single teaspoon of dirt trying to find a grave. The hoax of the child burials is now moving into fraud territory as some people are pocketing some serious coin from it.
We can’t just let this go. Bands across the nation are emulating the Tk’emlups approach as it’s a lucrative venture. It’s also causing more social division among people already in a societally dysfunctional state. At a couple of reserves with alleged grave sites, some excavations of alleged graves took place, only to discover that the graves did not exist. Rest assured, the bands won’t make that mistake again. They will just keep demanding money not to look.
Tk’emlups Chief Rosanne Casimir said in 2022 that the nation’s approach is an ongoing process of “exhumation to memorialization.” Ongoing indeed. Once questions began arising from people about how many children had been exhumed, the government leapt into the issue by sealing the records of the alleged Tk’emlups investigation. The band was supposed to produce regular reports of their progress in investigating the alleged graves as part of the conditions of their funding. Rather than admit the reports were either trash or non-existent, the government covered it up for the band. It’s not the band’s money. It’s taxpayers’ money, and we deserve to know where it went.
Plaintiff districts in Wisconsin funding suit outpace statewide per-pupil revenue

A group of five school districts, along with teachers’ unions and other advocacy groups, is suing the Wisconsin Legislature, alleging that the state is failing to provide adequate public-school funding.
The complaint also criticizes the state’s funding of parental choice programs, claiming such programs take aid from public schools (in reality, they do not reducefunding available to districts).
——
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Parents prepare for court battle to protect children from BBC ‘pro-trans bias’
The Bayswater Support Group (BSG), which represents more than 800 parents of primary-school-aged children and teenagers who believe they are transgender, has told Ofcom it will take legal action in the High Court unless it reverses its decision not to investigate their complaints about the corporation’s trans coverage.
The parents claim the broadcaster is promoting trans lifestyles to young people who are already vulnerable because of their age and mental health needs.
At times, the BBC has even appeared to encourage children to undertake irreversible medical transition, the parents claim.
The Telegraph revealed last November that among the parents’ complaints is that senior BBC managers dismissed their concerns and failed to take them seriously.
The Misuses of the University
The aging history professor—his beard graying, his posture slouching—parks his 1997 Honda and walks to his office at Johns Hopkins. Along the way he passes two giant glass cubes that, for the last five years, have slowly risen on the edge of campus. Limp signs on the fencing announce the opening of the SNF Agora Institute, by which, he’s informed, the university is “building stronger global democracy.”
How’s that going? he wonders.
In 2017, the institute was endowed with a $150 million gift from a Greek shipping fortune. The cost of the building, designed by Renzo Piano, has probably exceeded the entire donation. Scheduled to open in 2023, it was originally budgeted at $100 million—before the postpandemic surge of inflation. Walking past, the professor wonders what the final price tag will be, and who will pay for the faculty and staff who’ve already been hired by the institute, not to mention the robust programming. How much will it even cost to clean all that glass?
He pictures the trustees and donors at the building’s inauguration, whenever that happens. There will be soaring paeans to values of openness and transparency. It’s a glass building, after all. To him, the gargantuan structure doesn’t signal ancient Greek democracy as much as a Singapore convention hall or the atrium of a Dubai tower. It’s the placeless architecture of 21st-century global capital. He calls it “Airport Sublime.”
The day before the fall semester begins, the professor attends a convocation for new undergraduates. They look as eager as he feels jaded.
Johns Hopkins is launching its 150th anniversary celebration. When it was founded in 1876, American universities were still mostly finishing schools for children of the nation’s elite. Hopkins introduced the modern research university to the US, importing the model from Germany, helping reshape American higher education in its image.
Gladys West, Virginia-Born Navy Scientist Who Got Belated Credit for Helping Create GPS, Dies at 95
One frosty morning in January 1956, Gladys Brown and her younger brother, Nolan, drove north on Route 301 in Virginia. They needed a map to find their way to the Naval Proving Ground, a military research center on the banks of the Potomac River in Dahlgren, Va.
Brown, a 25-year-old mathematician later known by her married name of West, had worked for two years as a high-school teacher. Now she was starting a Navy job involving computers but had only a vague notion of what sort of mathematical work she would be doing.
A curious chat with Madison’s well funded k-12 Superintendent-Achievement….?
The 2024 referendum passed by a wide margin, but some people are feeling surprised by what they’re having to contribute to it. Do you have any response to some taxpayers’ concerns?
We don’t assess properties, so we’re not increasing the property value, and if property value goes up, of course the tax rate is going to go up as well. We told our community it was going to be a pretty historic investment, and sometimes, until you see that actual bill and what that impact will be on your property, I can completely understand why many people have kind of felt that sticker shock. We’ve taken a lot of calls, we’ve done some explaining, and have tried to really share that some of this is due to just the broken system of school funding in the state of Wisconsin.
——-
1998! Money and school performance.
A.B.T.: “Ain’t been taught.”
8,897 (!) Madison 4k to 3rd grade students scored lower than 75% of the students in the national comparison group during the 2024-2025 school year.
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $26,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Legislative Letter to Jill Underly on Wisconsin Literacy
